Targeting a key driver of IgA nephropathy
Sibeprenlimab is an investigational humanized IgG2 monoclonal antibody being evaluated for the treatment of immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (IgAN).

IgAN, also known as Berger’s Disease, is a chronic, progressive autoimmune kidney disease. IgAN is diagnosed in approximately 1 out of every 40,000 adults in the world each year. The progression of disease can vary from person to person and can involve blood and protein in the urine, high blood pressure, acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease, and the progressive decline in kidney function. Approximately 20-40% of IgAN patients will develop end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), or kidney failure, requiring dialysis or kidney transplant for survival.
IGA NEPHROPATHY (IGAN) OCCURS WHEN THE BODY GENERATES ABNORMAL VERSIONS OF IGA.
IgA is an antibody that is part of the immune system and when IgAN occurs, abnormal versions of IgA that are deficient in the sugar galactose (referred to as Gd-IgA1) are generated. The immune system misrecognizes Gd-IgA1 as a foreign antigen and generates auto-antibodies that bind to the Gd-IgA1, forming immune complexes, which are large pathogenic molecules that circulate through the blood and deposit in the kidney. The deposits of the immune complexes cause kidney inflammation and kidney damage.
There is no prevention or cure of IgAN. Current medical standard-of-care can cause unwanted side effects and may broadly and non-specifically suppress the patient’s immune systems, resulting in increased risk of infections and other complications.
HOW SIBEPRENLIMAB CAN HELP
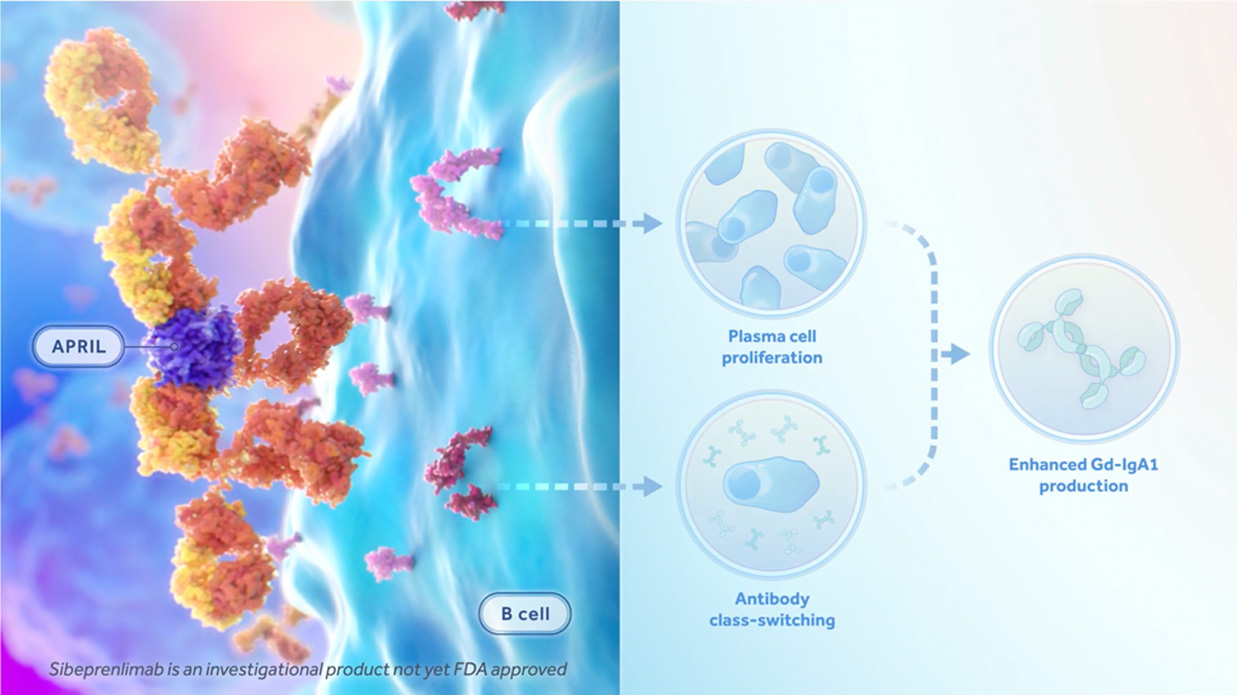
Sibeprenlimab reduces the production of Gd-IgA1 by binding to a specific signaling molecule called APRIL (short for “A Proliferation-Inducing Ligand”), which is believed to be a driver of IgA and Gd-IgA1 production. By binding and neutralizing APRIL, Sibeprenlimab may reduce the amount of IgA and Gd-IgA1. Lower levels of Gd-IgA1 may then result in reduced auto-antibody production, which in turn may result in fewer immune complexes, decreased immune complex deposits in kidney, and reduced kidney inflammation. By reducing the production of Gd-IgA1, Sibeprenlimab is believed to prevent further kidney damage and the progression to end stage kidney disease.
Click the link below to learn more about how Sibeprenlimab can help to fight against IgA Nephropathy.
PATIENT RESOURCES
Visit the care and advocacy partners below for information on kidney disease and patient advocacy and support.









